|
Home > Online Product Documentation > Table of Contents > Overview of DB-to-XML Data Sources Overview of DB-to-XML Data SourcesSQL/XML is an extension of the Structured Query Language (SQL) that allows you to query relational data, render query results as XML, and write modified or new data back to a relational database. Stylus Studio supports the SQL/XML standard by allowing you to create a DB-to-XML data source, a file that contains
The URL BuilderIf you need only to render an entire table or view as XML, use the URL Builder. Any time you need more control - writing your own SQL/XML or updating the relational database, for example - use a DB-to-XML data source. See Using the URL Builder for more information on the URL Builder Utility. In this sectionThis section covers the following topics: Supported DatabasesStylus Studio supports several relational databases, including: In addition, you can use DataDirect SequeLink Server, bundled with Stylus Studio, to connect to any ODBC data source. See Choosing a Database to learn more about specifying a database for a DB-to-XML data source. System RequirementsIn order to use DB-to-XML data sources, the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 1.4.x or greater must be installed on your machine. This feature also requires that you install the JRE with the optional module, Support for Additional Languages. You can verify whether or not this module has been installed by checking your JRE for these files: DB-to-XML Data Source ScenariosA DB-to-XML data source scenario is a group of customizable settings associated with a DB-to-XML data source. You use a scenario to specify connection settings, such as the You define these settings on the Scenario Properties dialog box. See Specifying Connection Settings to learn more about DB-to-XML data source scenarios. The DB-to-XML Data Source EditorYou use the DB-to-XML data source editor to specify database connectivity settings, and to compose the SQL/XML (queries and other actions) that you want to execute on the server.
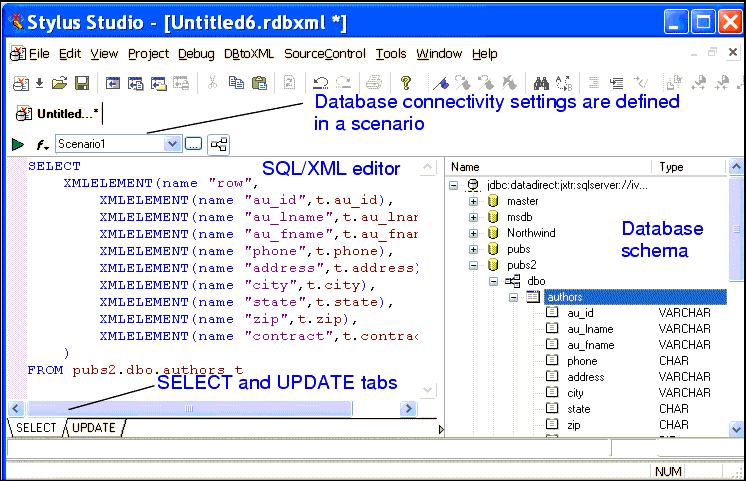
SQL/XML EditorThe SQL/XML editor is on the left side of the DB-to-XML data source editor. It consists of two tabs, SELECT and UPDATE, which you use to compose SQL/XML SELECT and, optionally, UPDATE and INSERT statements. You can type directly in the editor, or you can use drag-and-drop to automatically compose SQL/XML statements. See Composing SQL/XML in Stylus Studio to learn more about using the SQL/XML editor. Database Schema TreeThe database schema tree is on the right side of the DB-to-XML data source editor. Once you have established a connection to the database specified in the scenario, Stylus Studio displays a tree diagram of the database schema.
The database schema tree is displayed by default. You can hide it by clicking the
Show/Hide Database Schema button (
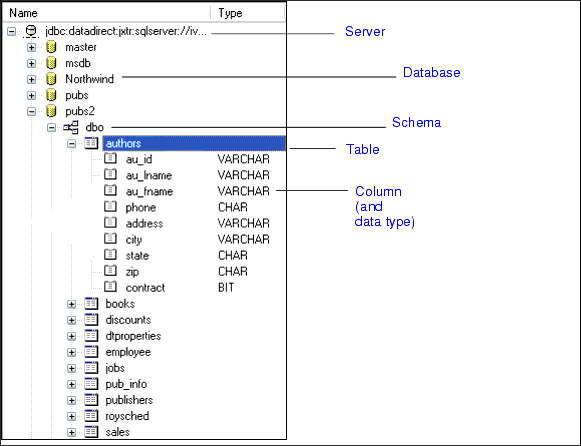
Information in the schema tree is displayed in a hierarchical fashion, starting with the server you specified in the scenario. Tables, views, and columns are displayed in database order; column data types are displayed in the Type column. Working with Relational DataStylus Studio can automatically create valid SELECT, INSERT, and UPDATE SQL/XML statements based on the objects you select from the database schema tree. In addition, your DB-to-XML data source can contain any valid SQL/XML statement defined on the SELECT or UPDATE tabs. The actions that can be performed by the SQL/XML you define in your DB-to-XML data source are limited only by the permissions of the username you use to log in to the database. See Composing SQL/XML in Stylus Studio for more information on this topic. Creating a DB-to-XML Data SourceThe process of creating a DB-to-XML data source in Stylus Studio involves the following steps:
1. Open a new DB-to-XML data source document in Stylus Studio. See
Opening a New DB-to-XML Data Source Document.
Stylus Studio displays the Scenario Properties dialog box.
2. Specify a scenario name (or accept the default) and the information needed to connect to the database server and log in to the database. This information includes
3. Save the scenario. Stylus Studio automatically connects to the database and logs you into the server. The database schema, table, view, and column information for the database you specified in the scenario appears in the DB-to-XML editor.
4. Compose the SQL/XML SELECT statement to query the database. (UPDATE and INSERT statements, which write modified data back to the database, are optional.) See
Composing SQL/XML in Stylus Studio.
5. Execute the query and review the XML it returns.
6. Optionally (if you have written SQL/XML to write new or modified data to the database), save the XML document returned by the SQL/XML query to write data back to the database. See
Working with Relational Data as XML.
The remainder of this chapter describes these steps in greater detail. |
XML PRODUCTIVITY THROUGH INNOVATION ™

 Cart
Cart