|
Home > Online Product Documentation > Table of Contents > Using Stylus Studio with Berkeley DB XML Using Stylus Studio with Berkeley DB XML
Stylus Studio allows you to access XML documents stored on Sleepycat Software's Berkeley DB XML database and to write documents back to the database. This section describes prerequisites, as well as the configuration and procedural information you need to get started. This section covers the following topics: OverviewStylus Studio can read and write well-formed XML documents ( .xml, .xsl, and so on) to/from Berkeley DB XML container files (containers). Containers typically have a .dbxml extension. In Stylus Studio, you reference external files using a URL. The URL used to access Berkeley DB XML files is dbxml:///container_pathname /filename .xml: For example, to access one of the sample files provided with Berkeley DB XML, you might enter the following in the URL field of the Stylus Studio Open dialog box: dbxml:///C:/samples/simpleExampleData.dbxml/Allspice.xml. Note that the container name ( C:/samples/simpleExampleData.dbxml in the example) appears in the URL field as if it were a directory name. This is because Stylus Studio treats Berkeley DB XML containers very much like directories, and the XML documents stored within a container are treated like files within a directory. You can save files back to the same container from which they were read, to a new container, or to some other file system (your local machine, for example).
Berkeley DB XML SupportStylus Studio supports Berkeley DB XML Version 1.2.1, and Version 2.0.7 and later. Usage SummaryThe process for using Stylus Studio with Berkeley DB XML consists of the following steps:
1. Make Berkeley DB XML
.jar and
.dll files accessible to Stylus Studio. See
Prerequisites for more information on this step.
2. Configure the
BerkeleyDBXML.xml file as described in
Configuring the BerkeleyDBXML.xml File.
3. Open Berkeley DB XML files in Stylus Studio as described in
Opening a File Stored on Berkeley DB XML.
4. Optionally, save your work back to Berkeley DB XML as described in
Saving a File Back to Berkeley DB XML.
Each of these steps is described in greater detail in the sections that follow. PrerequisitesIn order for Stylus Studio to access files stored on the Berkeley DB XML database, it must be able to access the .jar and .dll files shown in Table 75. Note that specific files vary based on the Berkeley DB XML version you are using, as shown in the following table.
These files are supplied by Sleepycat software - either as part of a pre-built binary distribution of Berkeley DB XML, or built by you if you received a source code distribution from Sleepycat. These files are not provided as part of your Stylus Studio installation. Once you have acquired these files, you must make them accessible to Stylus Studio. You do this by modifying your CLASSPATH and PATH environment variables as follows: These environment variables must be established before you start Stylus Studio. You cannot set them within Stylus Studio.
Saving Files to Berkeley DB XMLIn order to save files to Berkeley DB XML, you must first edit the settings in a configuration file. See Configuring the BerkeleyDBXML.xml File. Configuring the BerkeleyDBXML.xml FileYou need to configure the BerkeleyDBXML.xml file in order to be able to save XML documents back to a Berkeley DB XML container. Until you configure the BerkeleyDBXML.xml file as described in this section, any files you read from Berkeley DB XML are marked read-only and cannot be written back to Berkeley DB XML. The Berkeley Database EnvironmentThe Berkeley database has the concept of a database environment. The database environment is typically a directory that contains the log and lock files that provide support for transaction processing. This directory may also contain databases - files that contain user data. The containers in which Berkeley DB XML stores XML documents are examples of Berkeley databases and typically, though not always, have a .dbxml extension. To be able to determine what database environments exist in Berkeley DB XML, and which ones are associated with which containers, you need to These files are installed in the \bin\lib\sleepycat directory where you installed Stylus Studio ( c:\Program Files\Stylus Studio XML Professional Edition\bin\lib\sleepycat, for example). The BerkeleyDBXML.xml Configuration FileThe BerkeleyDBXML.xml configuration file contains elements that allow you to specify Berkeley DB XML database environments and directories: A finished BerkeleyDBXML.xml configuration file might look like this:
Omitting <dbdir> and <dbenv> elements
In some cases, it is not necessary do have any
If you use the
Specifying <dbdir> pathnames
Pathnames you specify for
The validate attribute
In Berkeley DB XML Version 2.0.7 and later, the
How to Configure BerkeleyDBXML.xmlTo configure BerkeleyDBXML.xml:
1. Open the
BerkeleyDBXML.xml configuration file in Stylus Studio.
2. Specify the
<dbenv> and
<dbdir> elements as described in
The BerkeleyDBXML.xml Configuration File.
3. Click
Validate Document
4. If the
BerkeleyDBXML.xml configuration file is valid, save your changes.
You are ready to use Berkeley DB XML with Stylus Studio. Open the Output WindowThe first time you perform an operation on the Berkeley DB XML, Stylus Studio tries to process the BerkeleyDBML.xml file. As the file is processed, messages are written to the Stylus Studio Output window. These messages identify which database environments and directories are being processed. This can be a useful way to verify which directories Stylus Studio is associating with which database environment and identify when you might need to make a change in the BerkeleyDBXML.xml file. Naming FilesFile-naming conventions vary between Berkeley DB XML V1.0 and V2.0.
Stylus Studio creates a unique pseudo-name for each named file in a container. Files without a name (supported only in Berkeley DB XML Version 1.2.1) are invisible to Stylus Studio. The pseudo-name consists of the file's name, concatenated with a pound sign (#) and the file ID assigned by Berkeley DB XML. Example - Berkeley DB XML V 1.2.1Consider the following files in a container as seen by Berkeley DB XML V 1.2.1: When you display this container in the Stylus Studio Open dialog box, only these files appear: Note that only duplicate file names are assigned a numeric ID. The fourth, unnamed, file, is not visible to Stylus Studio. Opening a File Stored on Berkeley DB XMLYou can open files stored on Berkeley DB XML in one of two ways:
To open a file stored on Berkeley DB XML:
1. From the Stylus Studio menu bar, select
File >
Open.
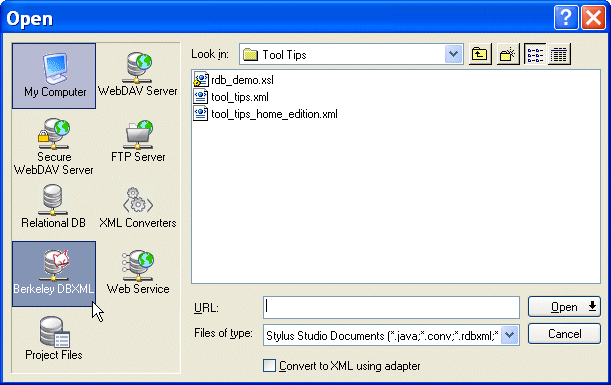
The Open dialog box appears. The left panel of the dialog box displays icons representing the file systems to which Stylus Studio has access, including one for Berkeley DB XML:
2. Click the
Berkeley DB XML icon.
The right side of the dialog box displays directories, containers, and any documents that match the extensions in the Files of type field.
3. Navigate the file system to locate the Berkeley DB XML database that contains the file you want to open.
4. Click the
Open button.
Saving a File Back to Berkeley DB XMLYou save a file to Berkeley DB XML as you would save a file to any other file system - click File > Save. If the document is not well-formed, Berkeley DB XML will not write it to the container.
Saving and ContainersBy default, File > Save saves the file back to the same container from which it was read. Additionally, you can
In any case, in order to save any work back to Berkeley DB XML, you must have previously configured the BerkeleyDBXML.xml file. See Configuring the BerkeleyDBXML.xml File. Validating Documents
If you are using Berkeley DB XML Version 2.0.7 or later, you can optionally have Sleepycat validate XML documents before saving them to the database. You do this using the
The syntax for the
Validation occurs at the container level; each container, specified as a node in the
BerkeleyDBXML.xml file, can have its own settings for the
Here, the
Schema requirementsIn order for Sleepycat to validate an XML document, the XML document must have its schema defined in an internal DTD. If the document does not contain a DTD, or references an external XML Schema, the document is not validated and will be saved if it is well-formed. Changing settings
Each time Stylus Studio starts, it reads the
BerkeleyDBXML.xml configuration file and uses its settings for the entire session. If you want to change the
Creating Containers with Stylus StudioTypically, you use Stylus Studio to access files in existing Berkeley DB XML containers. If you want, you can use Stylus Studio to create new containers. Stylus Studio creates a new container whenever
In order to create a new container: Node and Wholedoc ContainersBerkeley DB XML Version 2.0.7 and later supports Node and Wholedoc containers. Berkeley DB XML Version 1.2.1 supports only Wholedoc containers. Containers created by Stylus Studio are always created as Wholedoc containers. Usage TipsFollowing are some tips to help you work with Berkeley DB XML in Stylus Studio. Before Starting Stylus StudioBefore you start Stylus Studio, you must
Database Environment RecoveryDatabase environment recovery applications must have exclusive access to the database environment they are trying to restore. If you need to perform a database environment recovery, be sure to shut down Stylus Studio - and any other applications that might be using that database environment - prior to starting recovery procedures. |
XML PRODUCTIVITY THROUGH INNOVATION ™

 Cart
Cart